Warping Process in Textile Industry: Objectives, Types, Components and Mechanism
Warping Process in Textile
 |
Definition of Warping:
The parallel winding of yarn from cone or cheese packages onto a warp beam is called warping. This process is used to prepare the beam for the sizing process
Objectives of the Warping Process:
- To wound up a fixed length of yarn into a warp beam
- To increase the ability of yarn
- To increase the production
- To make it dynamic to the following process
- To increase the quality of the fabric
- To make reusable small packages
- To make convenient for sizing process
Requirements of Warping:
- The tension of all wound ends must be uniform and possibly constant during all the time of withdrawal from supply packages. Otherwise, the rate of breakage will be increased and the substance of ready cloth will be impaired.
- Warping should not hamper the physical properties of yarn. The tension should be moderate to allow the yarn to completely retain its elastic properties and strength. The yarn should not be subjected to sharp abrasive action.
- The surface of warping packages must be cylindrical. Therefore, the separating of yarn throughout the width of the warping must be as uniform as possible.
- Predetermine length of warping should be observed
- Higher production should be obtained during warping
Types of Warping
1. Sectional Warping:
In sectional warping, yarns are found in sections consequently to the warping beam as separate sheets or a section of equal length. Sectional warping is essentially a stages method, winding the area in succession in the warping drum and beaming the section of the complete warp from the winding drum onto the weaver's beam.
 |
| Fig: Sectional Warping |
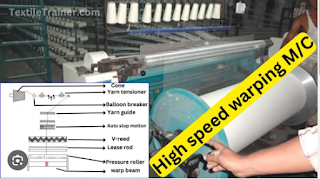
2. High Speed Warping:
In high-speed or direct warping, the yarns are wound parallel to the warping drum. Here, yarns are wound at once, and a simple flanged beam is used. HiHigh-speeding is usually regarded as a high-speed process particularly suitable for single-colored yarn. High-speeding is used for colored warp.
Difference Between High Speed and Sectional Warping
High-Speed Warping
- To produce common fabric in large quantities.
- Higher production speed
- Higher creel capacity
- To produce a warp beam from a large amount of warp yarn
- Weavers beam is produced after sizing
- A higher length of warp sheet is produced (15000-20000) m
- Only a flange bobbin is used
- Single-color yarns are used
- One stage is involved
Sectional Warping
- To produce a fancy fabric
- Lower production speed
- Creel capacity is low
- A small amount of yarn is used to produce a warp beam
- After sectional warping, weavers beam have been found immediately
- Warp sheet length is lower (100-200) m
- Cone or cheese bobbin is used
- Multi-colored yarn is used
- Two stage is involved
Components of Warping Machine
Warping Machine mainly consists of three components.
1. Creel
2. Head Stock and
3. Control Device
Creel:
A structure for holding supply packages in textile processing
Components of Creel
a. Yarn Cleaner: To remove the dust of yarn like slubs, neps, etc.
b. Stop Device: To stop the machine when the yarn is broken
c. Tensioner: To keep the yarn always in a remaining tension.
d. Indicator: To indicate the yarn breakage in the package.
e. Package Base: To house the packages.
Components of Head Stock
- Adjustable and Variable V-wraith: To control the width of the warp beam
- Measuring and Marking Device: Measures the amount of warp yarn on the beam and marks the yarn for definite use.
- Yarn Speed Controlling Device: To control the speed of yarn provided with a meter.
- Pneumatic and Hydraulic Pressure Unit: To press the warp beam with the surface contact of the driving drum.
- Break Assembly: It stops the machine's increase of yarn breakage.
- Driving Drum: The beam is in contact and control with the driving drum.
- Stop Motion: It is used to stop the machine after the required length of yarn is not wound on the beam
- Building Device: To control the space between the beam and the driving beam
- Beam Bracket: To support and hold down the beam
- Lease Rod: Used for separation of yarns individually.
Types of Creel
There are three main types of creel
1) Single-End Creel: A single-end creel is one in which a single package is associated with each and being wound. It does not necessarily mean that only an end is wound at one time. Creating takes a considerable time. It is essential to make it possible to transfer from one creel to another. This may be done by moving the headstock concerning some fixed creel. In this case, a movable headstock restricted the system to two creels which are known as duplicated creels. This is known as truck creels.
 |
| Fig: Single-End Creel |
2) Magazine Creel: The magazine package creel is multiple package creel. In the case of the magazine creel, two packages per end are used. The tail of one end in use is tied to the loading end of the other one. This proceeds creeping to proceed while the warping operation continues uninterrupted. The economic advantages of this creel are affect by the following factors:
a) Above 1% of the ends break at the time of transfer from one package to the other.
b) There can't be as many ends per end because of the space taken by the reverse packages.
3) Travelling or Multiple Package Creel: In the traveling package system, the package carriers move in loops so that, the yarn is being withdrawn from the outside of the loops. During changing the full package is moved as a body to the outside of the loop end and new packages are moved to the inside ready for replacement. Unfortunately, some threading time is needed at each changeover and this reduces the efficiency appreciably.
 |
| Fig: Traveling or Multiple Package Creel |
Faults and Defects of Warping:
- Warp off Centre of the Beam: If the creel wraith flanged is not carefully placed, this type of fault may occur.
- Uneven Surface of Warp Beam: This defect occurs due to a) Winding of a small no of ends or a larger beam. b) When of mixed count is wound. c) When the dents are bent. Hence to remove this fault ends of large no should be used of uniform count. The dents should be uniformly spaced.
- Cross Ends: During creeling if yarn is broken then the corresponding is formed.
- Smarl in the Warp: It forms for over tension. and twisting. So it should be given proper tension and twist.
- Ends Missing: After weaving yarn, if stop motion doesn't work. During warping, two or more yarns are missed. By proper counting, it can be removed.
- End Broken Down: During warping, if the yarn is broken down then this fault occurs. To minimize this fault yarn is to be joined very carefully.
- Hard Beam: A hard beam is formed if contact between the drum and roller is not at moderate pressure. So, pressure should be moderate.
- Unequal Size or Weight of Package: For this matter tension may vary in warp beam. All packages should be in same weight.
Warping Production Calculation:
A warping machine runs at 600m/min. Each beam contains yarn of 24000m and 430 ends. The no. of breakage 0.4 per thousand per 100m. Each breakage repair required 0.9 min. Every beam change requires 5 min and every beam+creel change requires 15 min. If there is sufficient yarn for 3 beam in every supply package. Calculate the efficiency?
Ans: Calculated Time = 24000/430 *3 = 120min
Stopage time for breakage = (0.4* 430/1000*24000*3/100)*0.9
=111.456min
Stopage time for beam and creel change = (5+5+5) = 25min
Actual time = (120+111.456+25) min
=256.456 min
Efficiency = Calculated Time/Actual Time *100%
=120/256.456 *100%
= 4.7%
Efficiency Loss = (100-47)%
=53%




Comments
Post a Comment