An Overview Of Vat Dye: Pretreatment, Recipe and Vatting Process
An Overview of Vat Dye
Vat Dye Definition:
VAT dyes are not insoluble in water. be used ton dyeing for treating with a reduction converted into water and modification. When agent, they Soluble aña loves compounds in the presence of alkalies. These love compounds are extremely substantive Jize 아 towards cellulose and ne-oxi- to insoluble the dyes in the presence of acid.
FASTNESS PROPERTIES OF VAT DYES
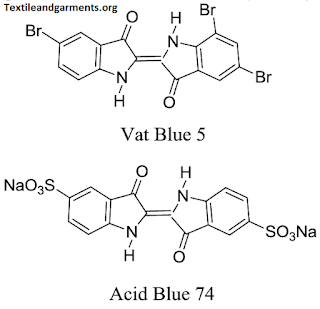
Chemical Structure of VAT Dyes:
Objectives of Vat Dyeing:
- To provide the desired colour.
- To obliterate the surface.
- To develop the newer design as per the market requirement
- To know about the function. of used chemicals in vat dyeing.
- To know different according to kinds of sharpe different specific parameter given
- To improve the weathering properties. and durability.
Recipe:-
1)Vatting:
Shade %-5%.
Sequestering Agent - 1cc/L
Hydrose (Na2S2O4) -3gm/L
NaOH - 2gm/L
Na₂ CO3- 3gm/L
PH-11.
Time - 15 minutes.
Temp - 70°C
MiL - 5:70.
2) Dyeing:-
Salt- (15-20) gm/L
Temp - 70°c.
Time - 30 minutes.
3) Oxidation:
Acetic acid- 1.5cc/L
pH (4.5-5.5)
Temp - 60°c.
Time - 15 minutes.
Function of Dyeing Chemicals:
Sequestering Agent - Remove the hardness from water.
Alkali (NaOH, Na2CO3) - It converts oil into water-soluble fatty acid and soap.
Salt- It acts as a catalyst, which accelerates the rate of absorption.
Hydrose- It acts as a reducing agent.
H2O2- It is used to insoluble the vat dye
Acetic acid -Hold the PH nang between (4.5-5.5).
Shade- Provide the desired colour.
Working Procedure of Vat Dye:
In vatting & dyeing, Aften measures the weight of the fabric, wake to take water which is seventy the aut times greater than 아 fabric. We carry overall vatting, dyeing and Oxidation into an aluminium vessel. Then we specific amount of sequestering agent, Shade, Hydnose, Naoh, Na, Con and for vatting and dyeing price where the temperature was 45 minutes. is 70°C an oxidation process. We take again. water which is several times greater than the actual amount of fabric. Then, mined specific amount of acetic acid, and Hydrozen peroxide where the heated temperature remained at 60°C for 15 minutes. Then, Fabric is taken for cold wash & dry.
Calculation
1. Vatting Process:
Fabric Weight = 7.66gm.
Weight of water = 536.2cc/L.
Sequestering Agent = 0.5362cc/L
Hydrase =3x0.5362
=1·60869.
NaOH = 2x 0.5362 = 1.07248.
Na2co3= 3x 0.5962 = 1.60889.
2. Dyeing Process
Salt = 208 x 0.5362 = 10.729 gm/L
Shade = 0.1159gm.
3. Oxidation
Weight of water = (60x7·66) =459.69cc/L
Acetic acid = 0.7cc/L
H2O2 = 2 x 0.459 = 0.91228cc/L
Recommendation:-
- During the weight of of fabric, the value wt measuring m/e must be seno.
- The amount of specific chemicals must be taken carefully.
- Hydrogen peroxide should be added after it is raised up to 60° temperature.
- We should use the mine..
- Fabrie aluminium versal should Remain in the drier for only (2-4) minutes.
Conclusion
From the experiment, We know about vatting, dyeing, and oxidation. the chemical used in this process definition of this chemical the dashed colon fabric buyer requirement and how according to VAT dyes




Comments
Post a Comment